Ban on RO Water Purifiers
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) directs the government to regulate RO-based water Purification Systems.
नेशनल ग्रीन ट्रिब्यूनल (एनजीटी) सरकार को आरओ-आधारित जल शोधन प्रणालियों को विनियमित करने का निर्देश देता है।
About:-
NGT directs MoEF&CC to establish regulations for RO-based water purification systems, resulting in Water Purification System (Regulation of Use) Rules, 2023.
एनजीटी ने MoEF&CC को RO-आधारित जल शोधन प्रणालियों के लिए नियम स्थापित करने का निर्देश दिया, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप जल शोधन प्रणाली (उपयोग का विनियमन) नियम, 2023 आएगा।
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has also notified the “IS 16240: 2023 Reverse Osmosis based point of Use Water Treatment System for Drinking Purposes
भारतीय मानक ब्यूरो (बीआईएस) ने पीने के प्रयोजनों के लिए “आईएस 16240: 2023 रिवर्स ऑस्मोसिस आधारित उपयोग जल उपचार प्रणाली” को भी अधिसूचित किया है।
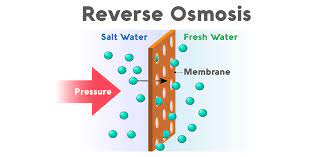 What is Reverse Osmosis (RO)?
What is Reverse Osmosis (RO)?
Reverse osmosis is a multi-stage water treatment process that removes contaminants from unfiltered water, or feeds water when pressure forces it through a semipermeable membrane. In the final stage, the RO membrane, water flows from the more concentrated side (more contaminants) to the less concentrated side (fewer contaminants) to provide clean drinking water. The fresh water produced is called the permeate. The concentrated water left over is called the waste or brine.
रिवर्स ऑस्मोसिस एक बहु-चरण जल उपचार प्रक्रिया है जो अनफ़िल्टर्ड पानी से दूषित पदार्थों को हटा देती है, या जब दबाव इसे अर्धपारगम्य झिल्ली के माध्यम से मजबूर करता है तो पानी को प्रवाहित करता है। अंतिम चरण में, आरओ झिल्ली, स्वच्छ पेयजल प्रदान करने के लिए पानी अधिक संकेंद्रित पक्ष (अधिक संदूषक) से कम संकेंद्रित पक्ष (कम संदूषक) की ओर प्रवाहित होता है। उत्पादित ताजे पानी को पर्मेट कहा जाता है। बचे हुए सांद्र जल को अपशिष्ट या नमकीन पानी कहा जाता है।
Osmosis:-
It is a physical phenomenon of water molecules from a dilute solution (high concentration of water) to a more concentrated solution (low concentration of water) across a selectively permeable membrane. The solvent moves to dilute the concentrated solution and equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. It is Limited to liquid molecules. Liquids move from regions of high to low concentration.
यह चयनात्मक पारगम्य झिल्ली में पानी के अणुओं के तनु घोल (पानी की उच्च सांद्रता) से अधिक सांद्र घोल (पानी की कम सांद्रता) में बदलने की एक भौतिक घटना है। विलायक सांद्र विलयन को पतला करने और झिल्ली के दोनों किनारों पर सांद्रण को बराबर करने के लिए आगे बढ़ता है। यह तरल अणुओं तक सीमित है। तरल पदार्थ उच्च सांद्रता वाले क्षेत्रों से निम्न सांद्रता की ओर बढ़ते हैं।
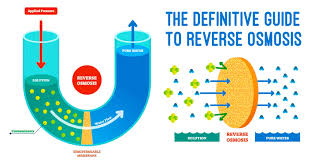 Distinction between osmosis and reverse osmosis:-
Distinction between osmosis and reverse osmosis:-
In their directional flow of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis entails the movement of water from a region of high to low water potential, whereas reverse osmosis involves water diffusion against the potential gradient. Additionally, while osmosis occurs naturally, reverse osmosis is a man-made process.
ऑस्मोसिस और रिवर्स ऑस्मोसिस के बीच अंतर एक अर्धपारगम्य झिल्ली में पानी के अणुओं के दिशात्मक प्रवाह में होता है। ऑस्मोसिस में उच्च जल क्षमता वाले क्षेत्र से निम्न जल क्षमता की ओर पानी की गति शामिल होती है, जबकि रिवर्स ऑस्मोसिस में संभावित ढाल के विरुद्ध पानी का प्रसार शामिल होता है। इसके अतिरिक्त, जबकि ऑस्मोसिस स्वाभाविक रूप से होता है, रिवर्स ऑस्मोसिस एक मानव निर्मित प्रक्रिया है।
Definition:
Osmosis: Osmosis is the spontaneous movement of solvent molecules (usually water) from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
Reverse Osmosis: Reverse osmosis is a process where external pressure is applied to force solvent molecules (water) from a region of higher solute concentration to a region of lower solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
Driving Force:
Osmosis: Osmosis is driven by the desire to equalize the concentration of solute molecules on both sides of the membrane, which is known as achieving osmotic equilibrium.
Reverse Osmosis: Reverse osmosis is driven by the external pressure applied to overcome the osmotic pressure and force water molecules through the membrane.
Direction of Movement:
Osmosis: In osmosis, water molecules move from the side of the membrane with lower solute concentration (hypotonic solution) to the side with higher solute concentration (hypertonic solution).
Reverse Osmosis: In reverse osmosis, water molecules are forced from the side with higher solute concentration (the feed solution) to the side with lower solute concentration (the permeate or product side).
Applications:
Osmosis: Osmosis plays a crucial role in biological processes, such as the movement of water in plant cells and the kidneys’ functioning.
Reverse Osmosis: Reverse osmosis is used in water purification systems to remove impurities and provide clean drinking water. It is also used in desalination processes to convert seawater into freshwater.
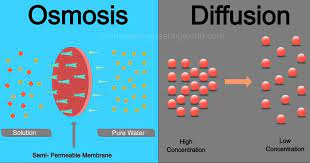 Diffusion:-
Diffusion:-
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. The overall effect is to equalize concentration throughout the medium. It occurs in any type of molecule, including liquids, gases, and solids. Molecules exhibit movement in both directions.
Diffusion:- Diffusion उच्च सांद्रता वाले क्षेत्र से कम सांद्रता वाले क्षेत्र की ओर कणों की गति है। समग्र प्रभाव पूरे माध्यम में एकाग्रता को बराबर करना है। यह तरल पदार्थ, गैस और ठोस सहित किसी भी प्रकार के अणु में होता है। अणु दोनों दिशाओं में गति प्रदर्शित करते हैं।

